From Inputs to Impact: The Role of Prompt Engineering in AI Performance
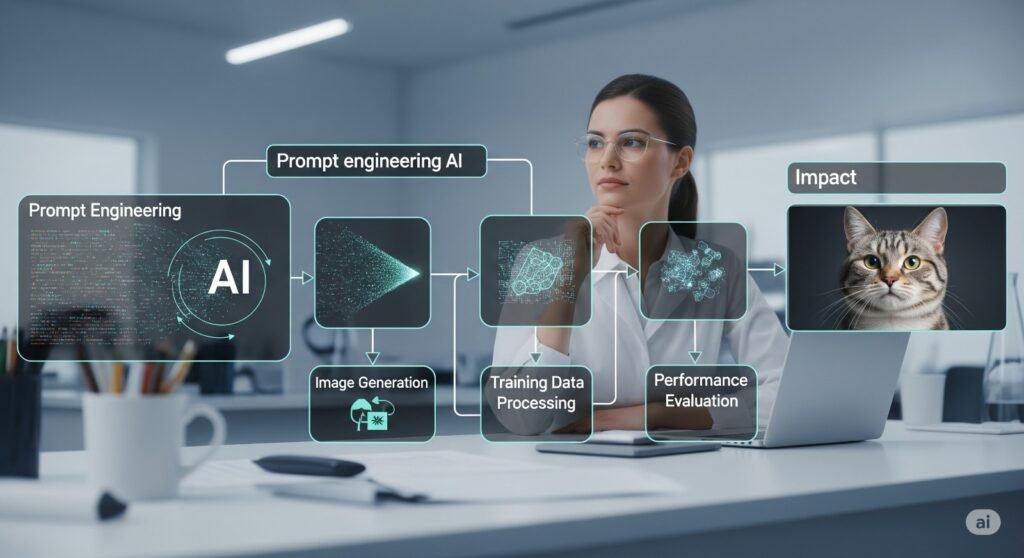
1. Introduction: The Subtle Science of Talking to Machines Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized the way we work, communicate, and innovate. From generating content to automating customer support, AI tools like ChatGPT, Claude, and Bard are rapidly becoming part of daily operations. However, the effectiveness of these systems heavily depends on one crucial factor—the quality of input they receive. This is where prompt engineering enters the scene. Often underestimated, prompt engineering is the strategic crafting of inputs (prompts) to guide AI models toward delivering precise, relevant, and contextually accurate outputs. In a hyper-digital world that thrives on AI performance, this discipline has emerged as the secret ingredient behind truly intelligent automation. 2. What Is Prompt Engineering? A Strategic Communication Layer Prompt engineering refers to the process of designing, structuring, and optimizing prompts to elicit high-quality responses from AI models. Rather than programming in traditional code, prompt engineers communicate through natural language or structured templates that guide machine reasoning. In simple terms, it is not just about asking the AI a question—it’s about asking it the right way. By understanding how large language models interpret language, engineers can construct prompts that align with business objectives, minimize error, and improve task outcomes. 3. The Growing Importance of Prompt Engineering Services As businesses increasingly adopt AI solutions, demand for prompt engineering services has skyrocketed. Companies using AI for content creation, customer support, data analysis, or workflow automation require highly tuned prompts to achieve consistent and scalable results. Prompt engineering is now critical across multiple industries—marketing teams rely on it to generate high-converting ad copy; customer service teams use it to fine-tune AI chatbots; and development teams leverage it to test and validate outputs before integrating AI into live products. In this context, prompt engineering is not optional—it’s essential. 4. How Prompts Directly Influence AI Performance AI models, especially those based on large language models (LLMs), don’t “think” like humans. Instead, they predict the most likely sequence of words based on the input they receive. A vague or poorly worded prompt may yield generic, irrelevant, or even inaccurate results. In contrast, a well-constructed prompt can produce precise, insightful, and task-aligned output. For example, the prompt “Write a blog about AI” might lead to a broad overview, while “Write a 1000-word blog in a formal tone explaining how AI is transforming healthcare” results in a more useful and targeted article. This demonstrates how prompt specificity directly enhances AI accuracy, tone, and relevance. 5. Common Use Cases Where Prompt Engineering Shines Prompt engineering is not confined to tech experts or developers. It serves an array of real-world applications that impact various business functions: Each of these applications benefits from structured input that guides the AI toward purpose-driven, high-impact output. 6. Prompt Engineering vs. Fine-Tuning: What’s the Difference? While prompt engineering involves crafting intelligent inputs, fine-tuning refers to modifying the AI model’s underlying parameters using domain-specific data. Fine-tuning requires large datasets, engineering resources, and model access—making it expensive and less flexible for everyday use. Prompt engineering, on the other hand, is faster, more cost-effective, and highly accessible. Businesses can optimize results without changing the core model, simply by adjusting the inputs. In many cases, prompt engineering alone can deliver results that rival those from fine-tuned models—especially for specific tasks like text generation, summarization, or classification. 7. Challenges and Limitations in Prompt Design Despite its potential, prompt engineering is not without challenges. One major issue is prompt sensitivity—minor changes in wording can lead to significantly different outputs. Additionally, AI models sometimes hallucinate or provide confident but incorrect responses, especially when given poorly designed prompts. Another challenge lies in scalability. A prompt that works well in one use case may not generalize across all users or languages. Therefore, prompt engineers must continuously test and iterate. Implementing version control, prompt libraries, and A/B testing can help mitigate these risks and improve consistency. 8. The Emerging Role of Prompt Engineers The rise of prompt engineering as a profession reflects its growing importance. Companies are now hiring dedicated prompt engineers to bridge the gap between business objectives and AI capabilities. These professionals possess a blend of linguistic creativity, technical insight, and business acumen. Moreover, new platforms and prompt engineering tools are emerging to support this role. From no-code AI builders to integrated development environments for prompt testing, these tools streamline experimentation and deployment, allowing engineers to fine-tune prompts at scale. 9. Best Practices for Effective Prompt Engineering To get the most out of prompt engineering services, businesses should follow a few best practices: By integrating these practices, companies can dramatically improve the performance and reliability of their AI implementations. 10. Conclusion: From Input to Intelligent Output Prompt engineering is no longer just a creative exercise—it is a strategic advantage in the age of artificial intelligence. As more organizations integrate AI into their workflows, the ability to shape machine behavior through smart prompts will become a competitive differentiator. From content generation and customer service to analytics and automation, prompt engineering allows businesses to maximize the value of their AI services while minimizing risk and inefficiency. In a world where AI’s power lies in its input, prompt engineering is the key to unlocking true impact.